#PDD#
Protein
Drug
Discovery
Antibody
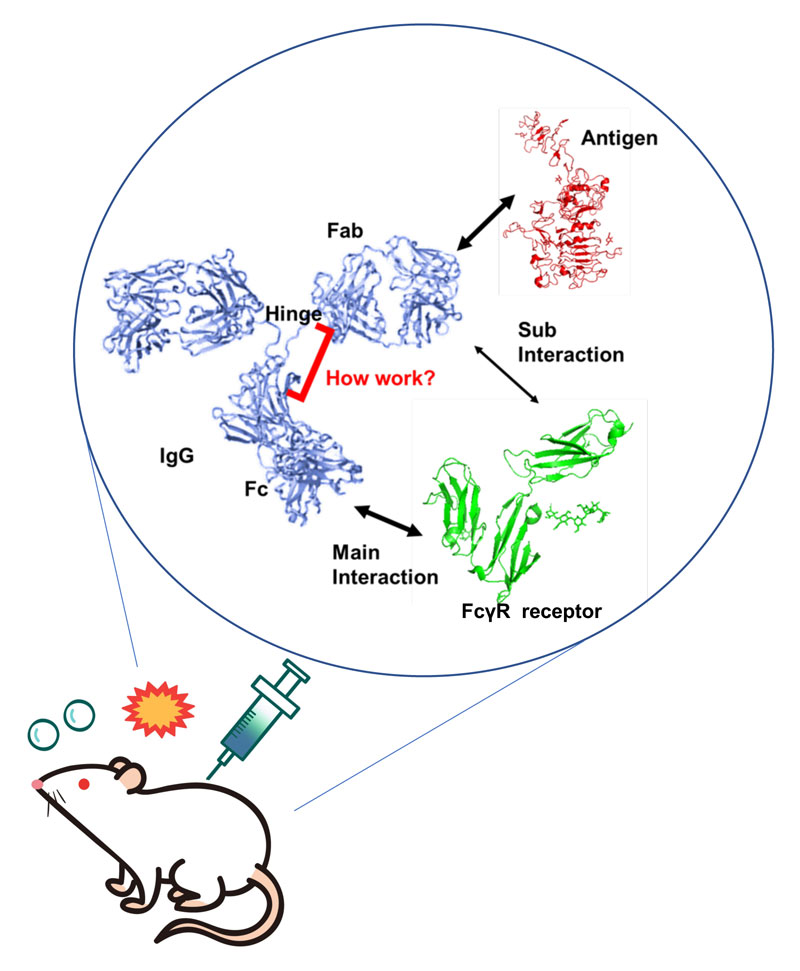
抗体の機能は、生体内に細菌やウイルスなどの異物が侵入した際に、それらを排除するように免疫システムを活性化させることです。抗体による免疫機能が発動される際には、抗原およびエフェクター分子との相互作用が必要不可欠であり、抗原を認識したという情報がエフェクター分子と結合する領域の状態に反映されているものと考えられています。しかしながら、その詳細なメカニズムは明らかとなっていません。ホセ研では抗体が免疫システムを活性化させる分子メカニズムの理解を目指しています。これにより、抗体を用いたバイオ医薬品の開発が進むことが期待されます。
The function of antibodies is to activate the immune system to eliminate foreign substances such as bacteria and viruses when they enter the body. Interaction with antigens and effector molecules is essential for the activation of immune function by antibodies, and it is thought that information about the recognition of antigens is reflected in the state of regions that bind to effector molecules. However, the detailed mechanism is not yet clear. Jose Lab aims to understand the molecular mechanism by which antibodies activate the immune system. This is expected to advance the development of biopharmaceuticals using antibodies.
Vaccine
ウイルスなどの異物由来の成分を人体に投与し、免疫システムに予めウイルスの存在を学習させるのがワクチンの役割です。ワクチンの投与による免疫システムの学習によって、ウイルスなどが人体に感染しても、早期に免疫システムが作動し、速やかに異物が排除されます。ホセ研では、ウイルスとウイルスを認識する抗体の構造情報に基づいて、より効力の高いワクチンを開発することに取り組んでいます。
The role of vaccines is to induce the immune system to learn in advance the existence of viruses by administering components derived from foreign substances such as viruses to the human body. The learning of the immune system by the administration of a vaccine enables the immune system to activate at an early stage of infection and quickly eliminate the foreign substance, even if a virus or other infectious agent infects the human body. Jose lab is working to develop more potent vaccines based on the structural information of viruses and antibodies that recognize viruses.